You need Q3 numbers for tomorrow's board meeting, so you submit a ticket to the data team. Two days later, the analyst asks for clarification. Another day passes before results finally arrive. Unfortunately, it’s already Thursday afternoon, and you needed that data on Tuesday.
Natural language business intelligence (BI) removes the bottleneck, so you can access insights whenever you need it — without having to learn about complex systems or new programming languages. You type your question in plain English and get answers in seconds. The AI writes the SQL for you and summarizes insights so you can focus on the question, not the code.
The user experience seems straightforward, but understanding the mechanics matters. This article explains how natural language BI works, where it fits into your data workflow, and how to evaluate whether your organization is ready for it.
What is natural language BI?
Natural language BI, also known as conversational BI, lets you interact with data using everyday language instead of writing SQL queries, building complex dashboards, or learning technical tools. You type "Which campaigns have the highest conversion rate to MQLS?" and get results in seconds.
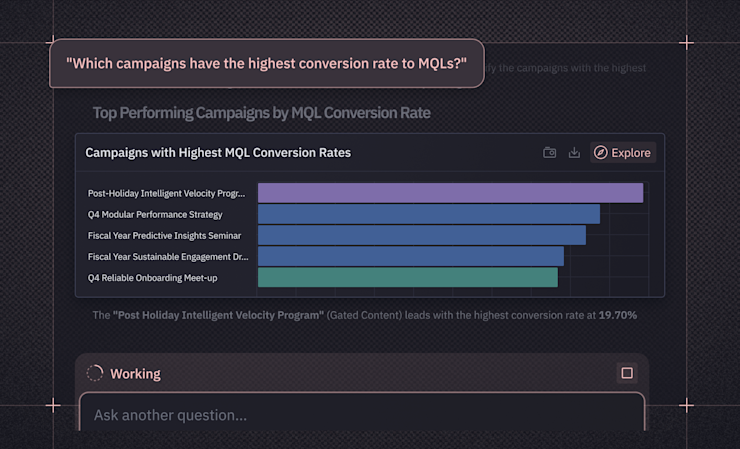
The core technology behind natural language BI is natural language processing (NLP). NLP allows AI systems to understand human language — i.e., how humans naturally speak and write — and translate it into machine-executable commands. When you ask a question, the AI parses your words, identifies what you're asking for (time period, metrics, groupings), maps those concepts to your actual database structure, generates SQL, and returns results. The technical work happens in the background.
Natural language BI shines when you need answers that don't fit existing dashboards. For instance, when a product manager notices feature adoption dropped 15% last week and needs to understand why before the team meeting in an hour.
Natural language BI makes data more accessible compared to traditional BI workflows, where you have to build dashboards weeks ahead or find the right one (if it exists), write SQL (if you know how), or submit a ticket to the data team and hope for a quick turnaround. Natural Language BI lets you ask directly, drill into segments driving the change, and test hypotheses in a single session.
Apart from benefiting non-technical users, natural language BI also helps data teams. They stop having to answer repetitive questions quarter over quarter and focus instead on building the infrastructure that makes accurate answers possible. This means defining metrics, documenting business logic, and setting up governance rules.
How natural language BI works
Natural Language BI usually uses a text-to-SQL pipeline that converts plain English into executable database queries.
Here's what happens under the hood:
The model parses your question and maps it to schema
When you type a question, a large language model first parses the text to identify what you're asking for. It extracts entities (like "Q3" or "enterprise customers"), metrics (like "revenue" or "conversion rate"), and operations (like "compare," "trend," or "group by"). The model then maps these concepts to your actual database schema and context assets like semantic models and rules files. For examples, it matches "revenue" to the specific table and column where that data lives.
The semantic layer translates business terms to SQL
A semantic layer sits between the AI and your raw data. It defines what business terms actually mean: "revenue" is SUM(amount) WHERE status = 'completed', "active customer" is anyone with a transaction in the last 90 days. This layer drastically improves the accuracy of the AI, codifying the metrics and reducing hallucinations.
Semantic layers also define relationships between tables, specify which joins are valid, and flag which data sources are trustworthy. When teams define metrics differently, semantic layers incentivize standardization of metrics, creating a single source of truth. That way, the AI can query the semantic model and not the raw tables, which keeps results consistent across every question.
The system generates SQL and runs it against your warehouse
Once the model understands intent and has schema context, it generates SQL. Modern systems generate multiple queries, score them for correctness, and select the best option. Some systems run validation checks before execution to catch obvious errors like invalid column references.
The query runs against your data warehouse (Snowflake, BigQuery, Databricks, or others), and results return to the interface. The entire round trip typically takes a few seconds, though complex queries against large datasets can take longer.
Conversational systems track context across questions
Single-query systems treat each question independently. Conversational systems maintain context across a session, tracking what you've already asked and what results you've seen. These systems can handle everything from follow-up questions and topic shifts to references to previous answers.
Looking for a tool that uses this conversational approach? With Hex Threads, you can ask questions like, "show revenue by product line," then follow up with, "which regions drove growth?" without restating the context. The system uses the context from everything asked in the Thread and shows you the generated SQL and the reasoning behind each step so you can verify the logic.
Use cases for natural language BI
Natural language BI shines in moments where traditional BI falls short — when you need answers faster than dashboards can provide, when the question doesn't fit a pre-built report, or when exploration needs to happen collaboratively across teams. Here are some of our favorite use cases:
Investigate questions that don't have dashboards
Natural language BI handles ad hoc investigation where dashboards don't have the predefined filters or data to answer their next question. You can ask why a metric spiked, drill into the segments driving the change, and test hypotheses, all in one session. The iterative back-and-forth with your data team that would take weeks through a ticket queue happens in minutes.
Pull your own reports without tickets
Natural language BI opens the door to true self-service reporting. Business users can pull standard reports, customize filters, and explore segments without submitting requests to the data team. The data team can then shift from processing an endless ad hoc queue to building the context layer that powers accurate answers. Some organizations use embedded analytics to extend this self-service capability directly to their customers.
Prepare for meetings with informed hypotheses
Natural language BI lets you pull fresh data right before a meeting rather than relying on slides prepared days earlier.
Let’s say a revenue operations manager notices a sales rep struggling to close new business this quarter. Before their weekly pipeline review, that manager can use natural language BI to ask: "Why has this rep been struggling to close new business?" The system can then surface insights like lower average deal size, longer sales cycles, or shifts in prospect industry mix. That way, the manager comes to the meeting with a data-backed hypothesis on why performance changed.
Make decisions in real time
Natural language BI removes the friction that makes on-the-spot data access impractical. You can answer questions during calls, validate assumptions mid-conversation, and check numbers from your phone. No dashboard hunting, no filter configurations, just ask and get the answer.
Here’s an example:
Hex's Growth Marketing Lead needed to evaluate San Francisco billboard placements. He used Threads (Hex’s conversational BI tool) to ask for prospect addresses. In return, he got an interactive map of where target accounts were located, and had his answer in a couple hours.

No data team ticket, no waiting.
Explore data together with your team
Natural language BI goes hand-in-hand with collaborative analysis. One person starts a thread, shares it with colleagues, and others add follow-up questions in the same conversation. In Hex, these conversations transition directly into Notebooks when you need deeper analysis. This team-based workflow keeps the entire exploration history connected.
Getting started with natural language BI
Step one to getting started with natural language BI is getting your data ready before you roll out the new tech to users. Then focus on governance and change management as more people start using the new tools.
Start with trusted tables and a prioritized use case. Every team has at least a few "golden tables" that are clean, well-documented, and trusted. Use these as your starting point, focusing on a specific line of business or use case. Once that's working, you can expand to additional tables and clean data where needed.
Then, as you start to scale, start thinking about data governance. Define who can access what, spot-check AI outputs, and create feedback loops for incorrect results. For change management, start with lunch-and-learns, build a library of example queries, and identify early adopters in each department who can show wins to their peers.
The future of data interaction
Natural language interfaces are becoming standard. Gartner predicts 75% of new analytics content will use generative AI for contextual intelligence by 2027. If that isn’t a signal that conversational interfaces are about to become the new norm, we don’t know what is.
The platforms that win will combine accessibility with governance. Conversational interfaces lower barriers for simple questions. But complex analysis still needs notebooks and code.
Hex bridges this gap. Threads provides conversational analytics for self-service exploration. Notebooks give data teams analytical depth. Data Apps let you publish interactive dashboards that stay connected to live data.
Behind the scenes, Hex gives data teams the observability to see which questions people are asking and a suite of context curation tools to ensure those questions get trusted answers. Build semantic models directly in Hex or sync them from your existing sources — either way, you're powering conversational BI with governed data.
Request a demo or sign up for a free trial today to see how Hex can make everyone in your organization a data person.